2020-05-18T00:00:00.000+00:00
Predicting conversion to wet age-related macular degeneration using deep learning
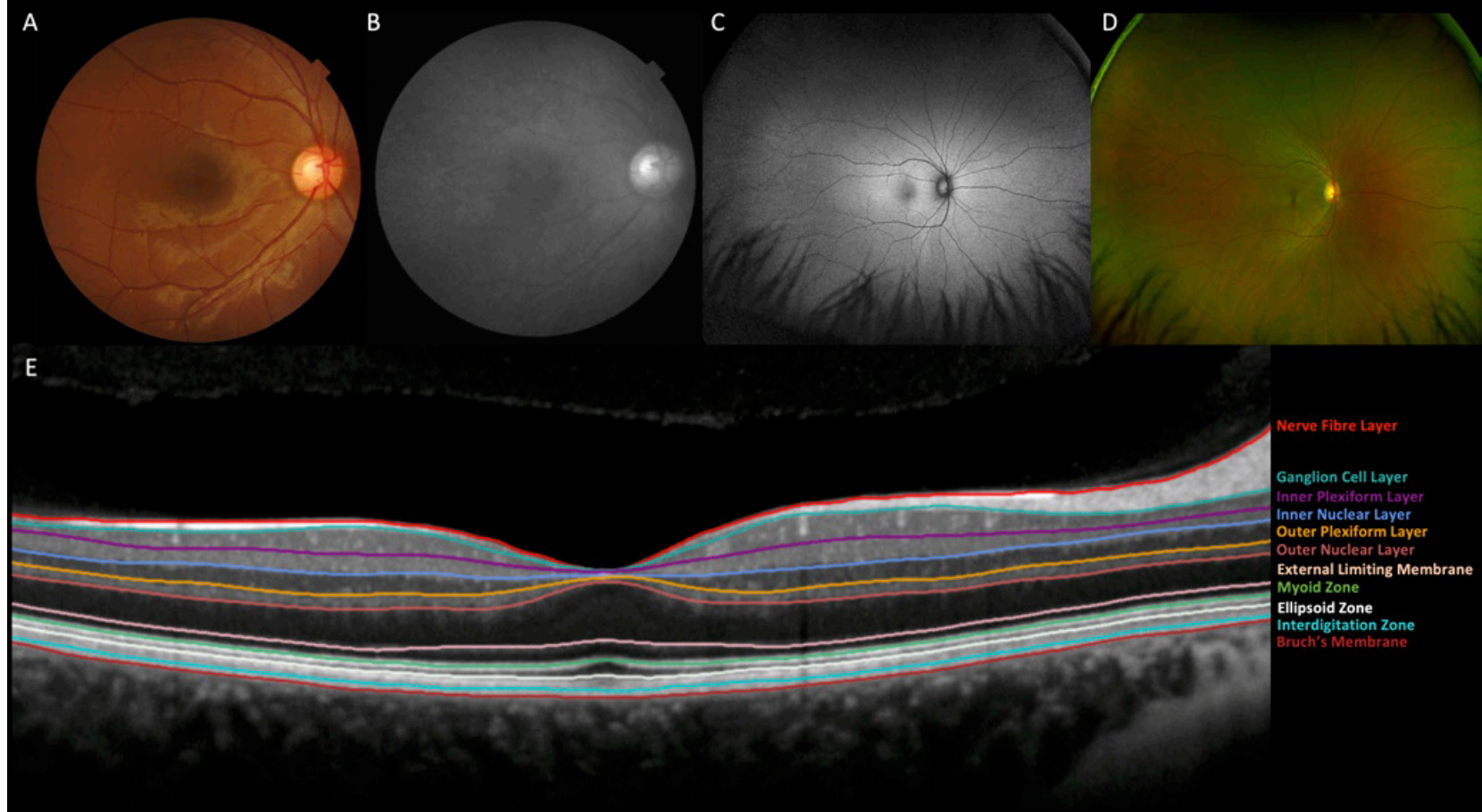
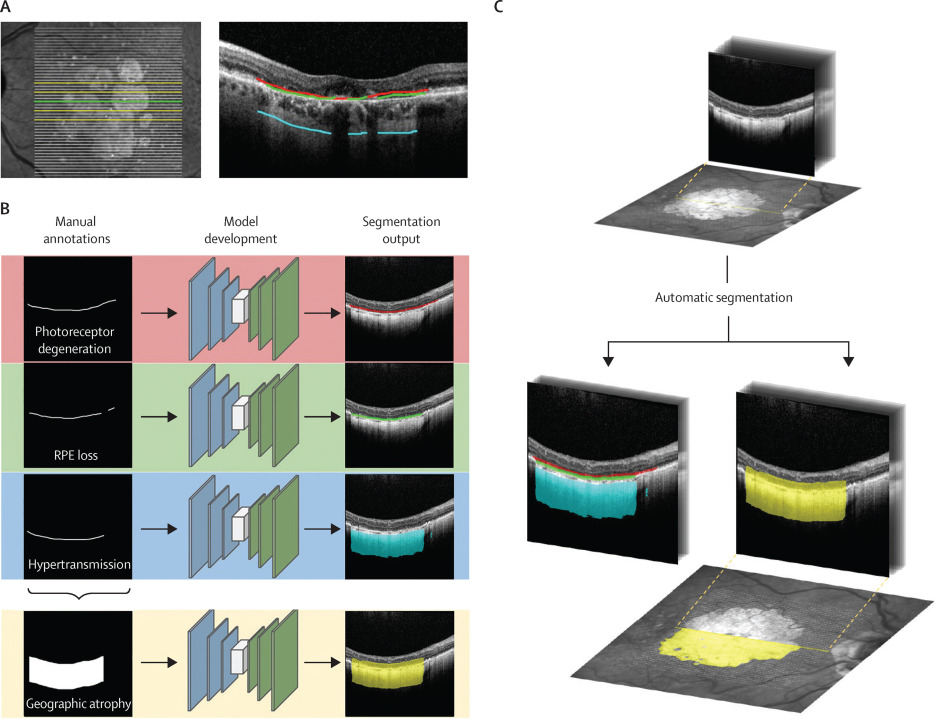
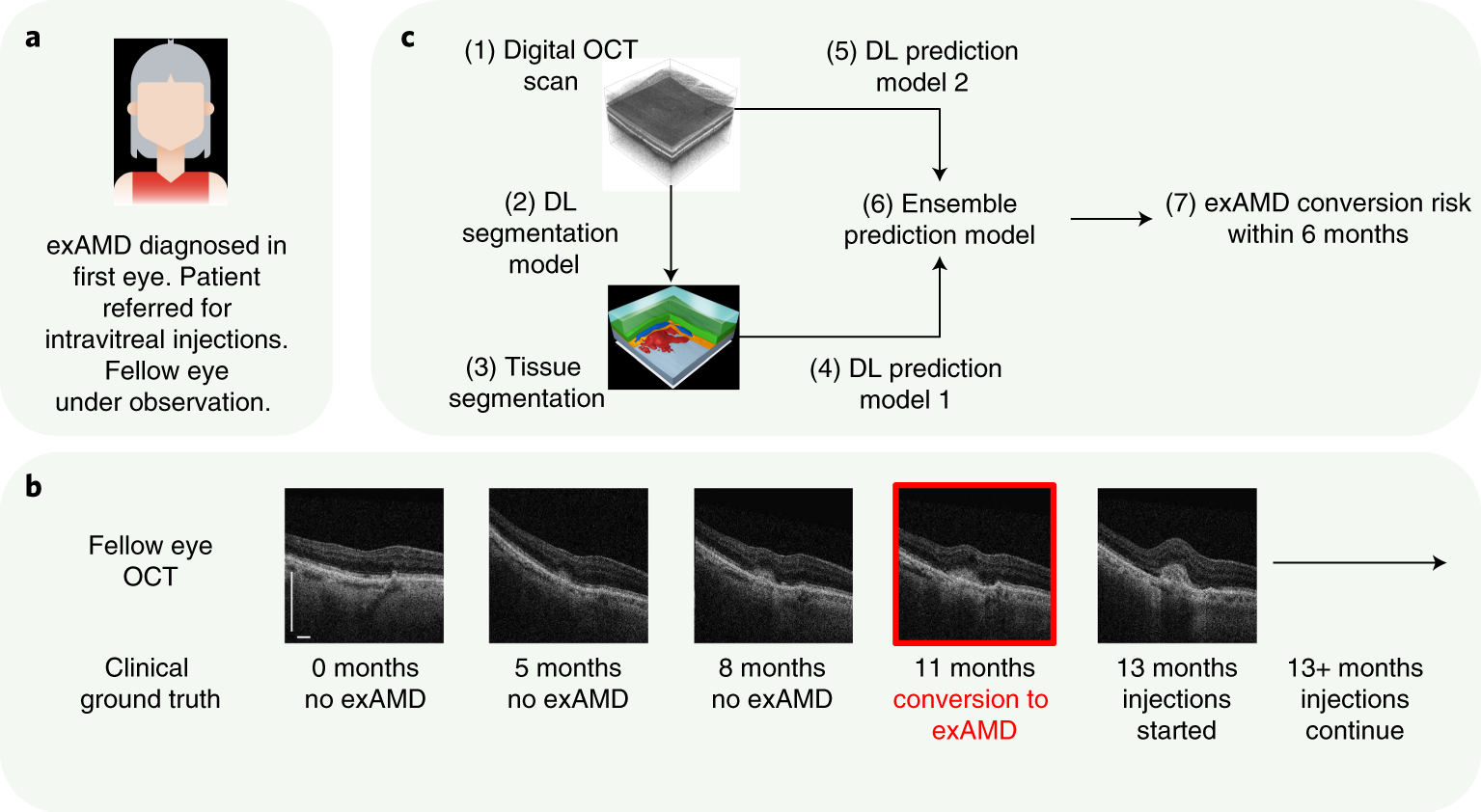
Progression to exudative ‘wet’ age-related macular degeneration (exAMD) is a major cause of visual deterioration. In patients diagnosed with exAMD in one eye, we introduce an artificial intelligence (AI) system to predict progression to exAMD in the second eye. By combining models based on three-dimensional (3D) optical coherence tomography images and corresponding automatic tissue maps, our system predicts conversion to exAMD within a clinically actionable 6-month time window, achieving a per-volumetric-scan sensitivity of 80% at 55% specificity, and 34% sensitivity at 90% specificity. This level of performance corresponds to true positives in 78% and 41% of individual eyes, and false positives in 56% and 17% of individual eyes at the high sensitivity and high specificity points, respectively. Moreover, we show that automatic tissue segmentation can identify anatomical changes before conversion and high-risk subgroups. This AI system overcomes substantial interobserver variability in expert predictions, performing better than five out of six experts, and demonstrates the potential of using AI to predict disease progression.