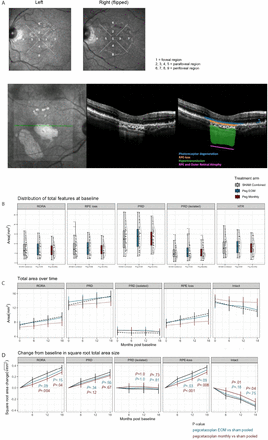
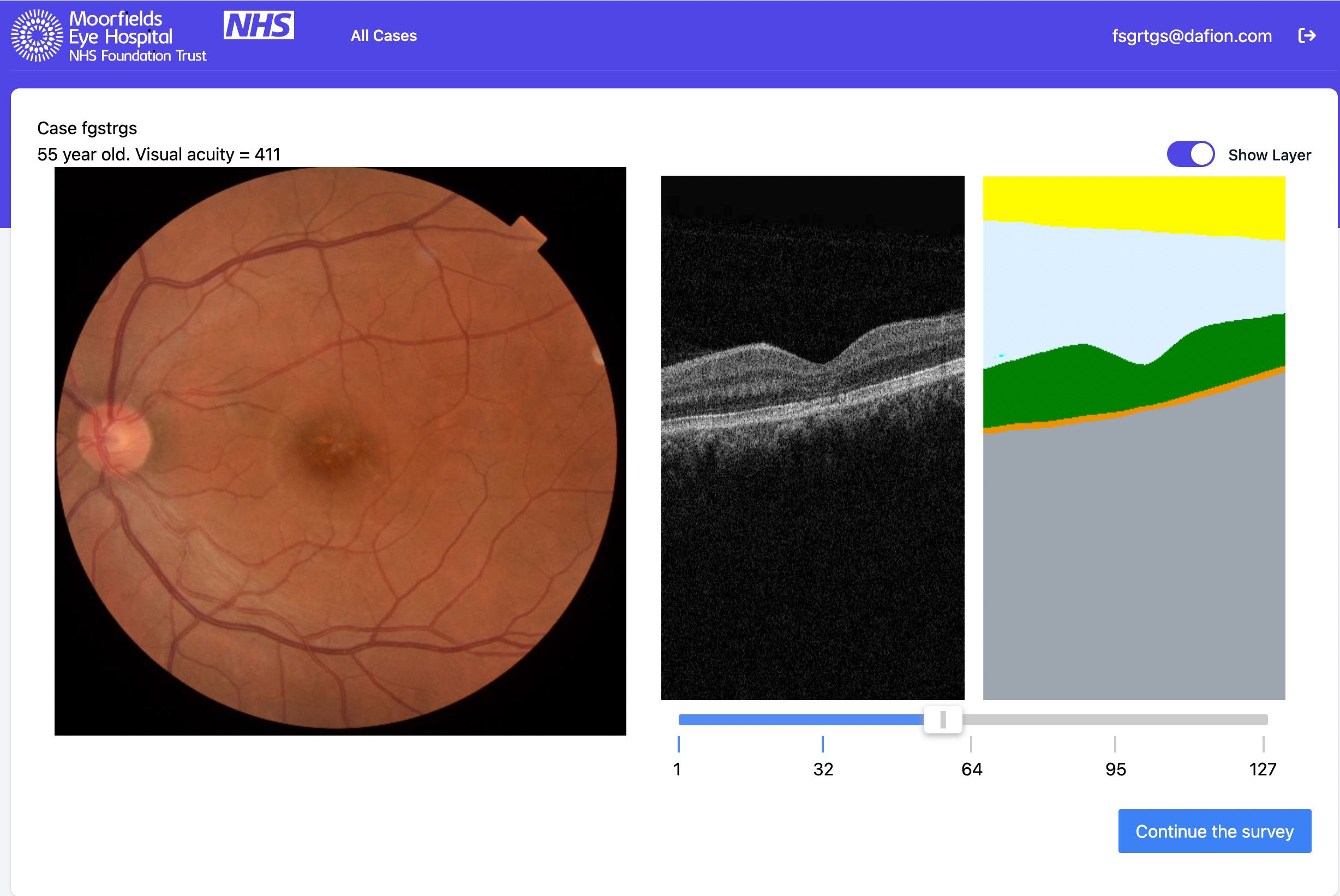
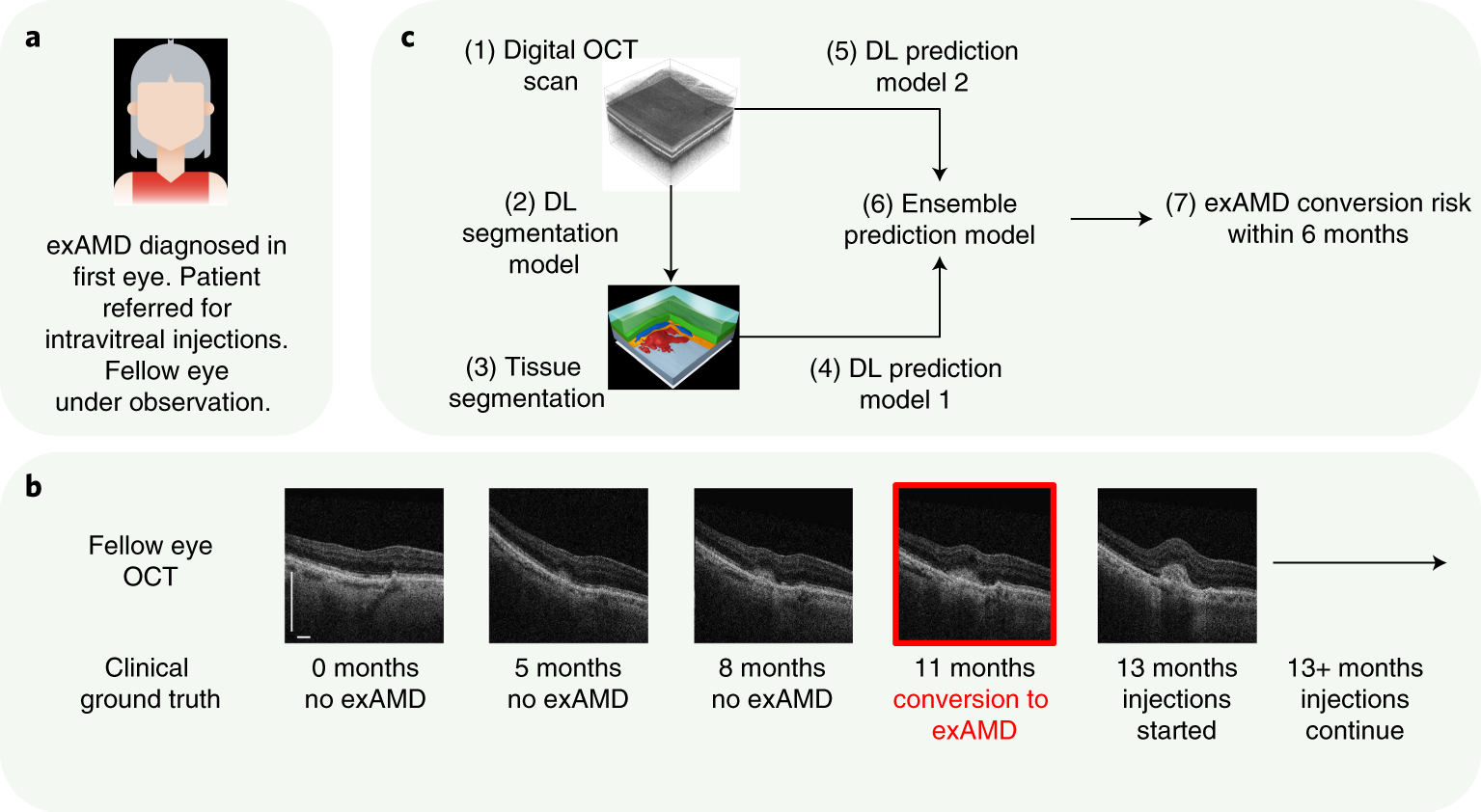
Deep-learning automated quantification of longitudinal OCT scans demonstrates reduced RPE loss rate, preservation of intact macular area and predictive value of isolated photoreceptor degeneration in geographic atrophy patients receiving C3 inhibition treatment
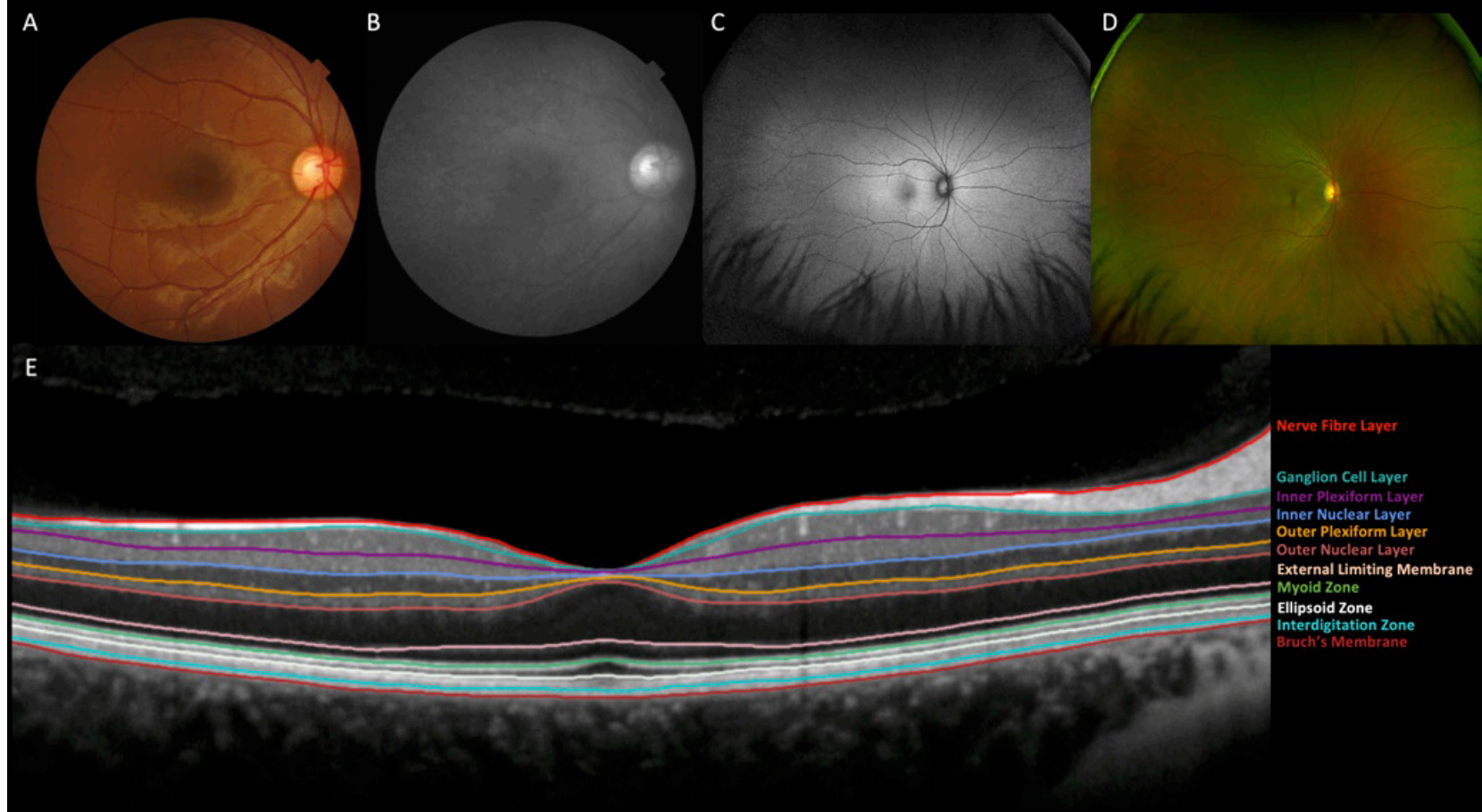
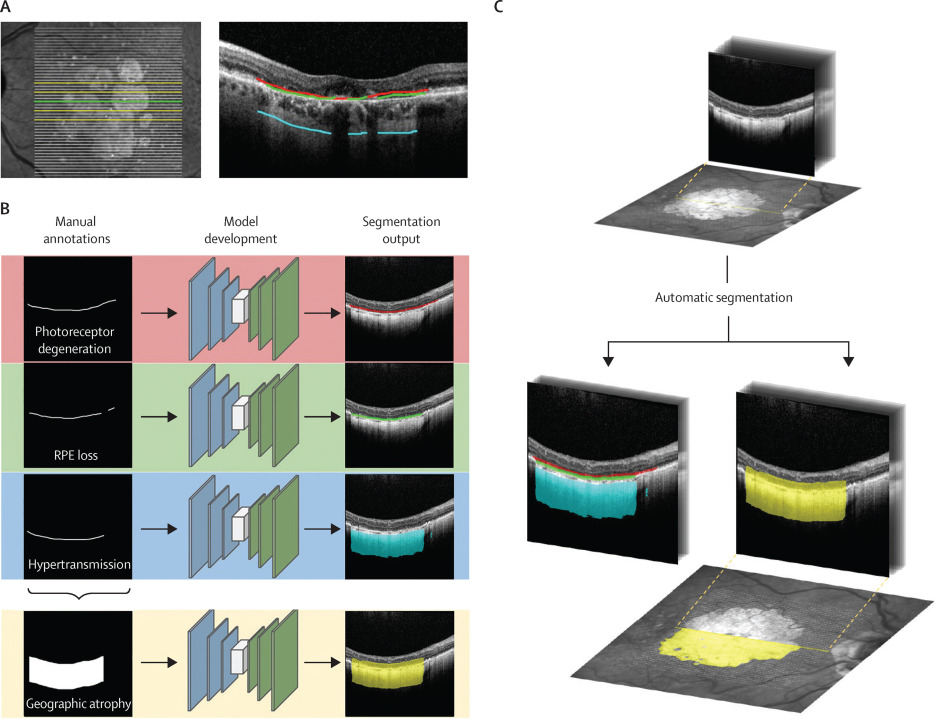
To evaluate the role of automated optical coherence tomography (OCT) segmentation, using a validated deep-learning model, for assessing the effect of C3 inhibition on the area of geographic atrophy (GA); the constituent features of GA on OCT (photoreceptor degeneration (PRD), retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) loss and hypertransmission); and the area of unaffected healthy macula. To identify OCT predictive biomarkers for GA growth. The OCT evidence suggests that pegcetacoplan slows progression of cRORA overall and RPE loss specifically while protecting the remaining photoreceptors and slowing the progression of healthy retina to iRORA.